Hub Motor vs. Mid-Drive E-Bikes – Which is good?
When choosing an ebike, the decision between a mid-drive or hub motor design is crucial. It directly impacts the price, ride quality, and overall performance of the bike. Our comprehensive guide outlines the key differences between these motor types, providing a thorough analysis of the pros and cons. We cover performance metrics, maintenance requirements, ride quality, handling, range, and more.
We want to help you to make a well-informed selection that fits your riding style by arming you with this knowledge. With this article our principal aim is to assist you in selecting the ideal ebike that provides the best mix of strength, efficiency, and price.
The distinct benefits and drawbacks of each hub drive system and mid-drive system should be carefully considered when choosing one for your electric bicycle. To make the best choice, it’s recommended to assess the trade-off between cost and performance, as both factors play a significant role in determining the most suitable option for your needs.
What is Hub Motors?
The hub motor, known by various names such as wheel motor, wheel hub drive, hub motor, or in-wheel motor, refers to an electric motor integrated into the hub of a wheel. It operates by directly driving the wheel, providing a compact and efficient means of propulsion.
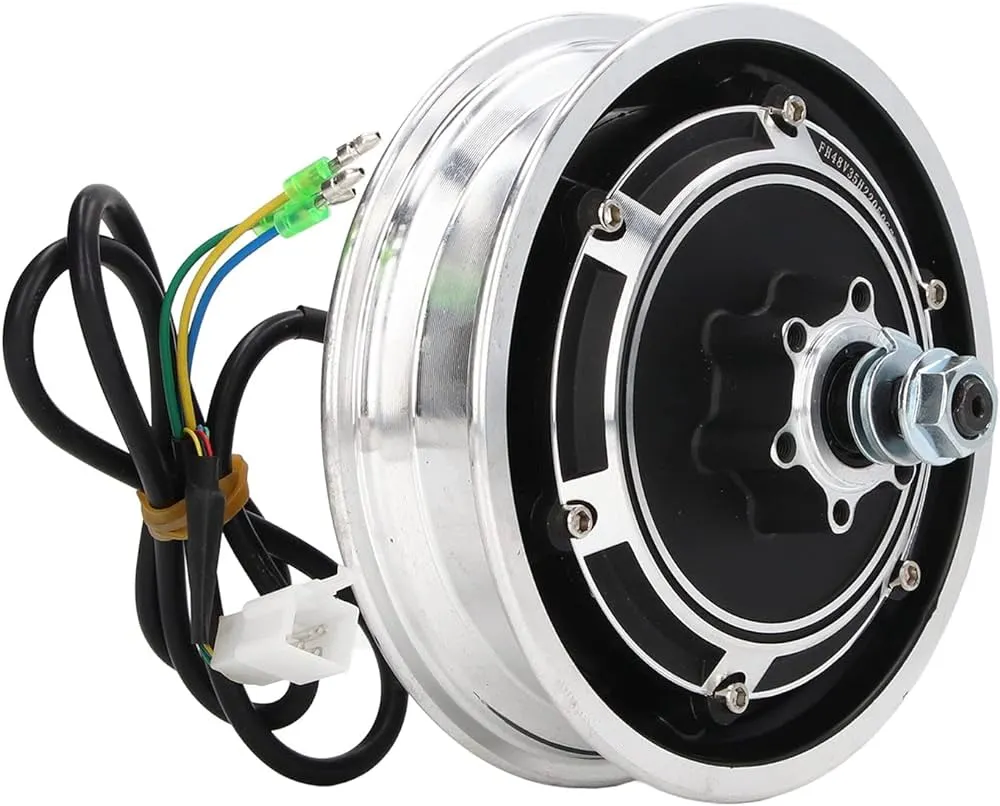

It istypically found on the rear wheel of electric bikes. To bridge the speed differential between the motor and the bike wheels, a gear reduction system connects the hub motor and the stator. This gearing mechanism allows the motor to operate efficiently at its preferred high speed, generating multiple rotations internally for every revolution of its outer case. Further Hub motors are of two types:
1.Direct-drive hub motor:
A direct-drive hub motor consists of an axle that serves as both the motor axle and stator. The copper windings are firmly attached to this axle, forming the stator assembly. On the outer shell of the hub motor, magnets are positioned. When electric current flows through the stator, it generates a magnetic field, prompting the magnets to undergo movement. Consequently, the entire motor shell rotates, propelling the e-bike forward.
2.Geared hub motors:
In contrast, geared hub motors employ a planetary gear reduction system that connects their cases to the stator. With this setup, for each revolution of the motor case, the internal motor actually rotates multiple times faster. This arrangement enables the motor to operate at higher speeds, enhancing its efficiency, while enabling the wheel to rotate at a relatively slower speed for effective driving.
Advantages of Electric Bicycles with Hub Motor
Cost-effective:
Hub motor e-bikes are typically less expensive than mid-drive motor e-bikes.
Throttle control:
Hub motors often have a throttle feature, allowing riders to engage the motor without pedaling.
Regenerative braking:
Some hub motors can offer regenerative braking, which helps recharge the battery when the brakes are applied.
Reduced stress on gears:
Hub motors eliminate the need for gears and chains, reducing stress on the drivetrain and minimizing maintenance requirements.
Disadvantages of Electric Bicycles with Hub Motor
Lower range:
Hub motors tend to have a lower range compared to mid-drive motors. This is because the motor’s weight is concentrated in the wheel, leading to increased energy consumption, and reduced overall efficiency.
Reliability concerns:
Hub motors can put torsional stress on the spokes of the wheel, which may lead to potential wheel breakage or damage. This can be a reliability issue, particularly when encountering rough terrains or if the e-bike is carrying heavy loads.
Difficulty climbing steep inclines:
Hub motors lack gearing systems, which can make it challenging to climb steep hills. The absence of gears means the motor cannot provide the same level of torque as mid-drive motors, limiting the e-bike’s climbing ability.
Increased weight:
Hub motors add weight to the wheel assembly, making the e-bike generally heavier compared to mid-drive motor e-bikes. This extra weight can impact the bike’s handling, maneuverability, and overall riding experience.
Uneven power output:
Hub motors may exhibit uneven power output, particularly at low speeds or during initial acceleration. This can result in a less smooth and consistent riding experience, especially when starting from a stationary position or navigating at slow speeds.
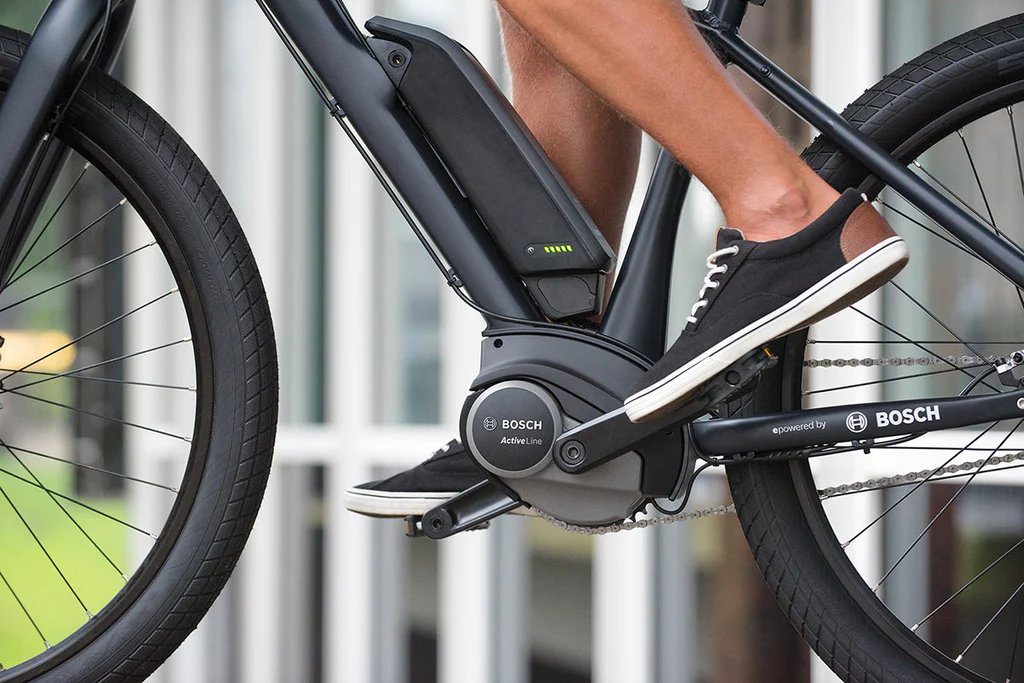
What is Mid Motor?
A mid-drive motor in an e-bike refers to the placement of the electric motor in the central part of the bicycle’s frame, near the crankset or bottom bracket. Unlike hub motors, which are placed in the front or rear wheel hub, mid-drive motors provide power directly to the bike’s drivetrain by engaging with the chain or belt drive.

Advantages of Electric Bicycles with Mid Motor
Centered and Balanced Feel:
Mid-drive motors are positioned in the central part of the bike frame, resulting in a balanced weight distribution. This contributes to a more centered and balanced feel while riding, improving overall stability and manoeuvrability.
Smooth and Consistent Power:
Mid-drive motors offer smooth and consistent power delivery. By leveraging the bike’s gears, the motor adjusts its output to match the rider’s pedaling cadence and the terrain. This seamless integration provides a natural and responsive riding experience.
Maintains a Non-Ebike “Feel”:
E-bikes with mid-drive motors often maintain the look and feel of traditional bicycles. The motor’s central placement allows for a less conspicuous appearance, as it doesn’t visibly alter the bike’s external design. This can be appealing for riders who prefer a more traditional or inconspicuous look.
Longer Range Due to Increased Efficiency:
Mid-drive motors are highly efficient in converting battery power into forward motion. By utilizing the bike’s gears, they optimize power usage and reduce energy wastage. This increased efficiency translates to longer battery range, allowing riders to cover greater distances before needing to recharge.
Lighter Than Most Hub Motor E-bikes:
In general, mid-drive motor e-bikes tend to be lighter compared to their counterparts with hub motors. The central motor placement allows for better weight distribution, reducing the overall weight of the bike. This lighter weight contributes to improved handling and maneuverability, especially when navigating tight turns or challenging terrain.
Disadvantages of Electric Bicycles with Mid Motor
Typically, More Expensive:
E-bikes with mid-drive motors tend to be more expensive compared to e-bikes with hub motors. The complexity of the mid-drive system, along with the integration of the motor with the bike’s drivetrain, can result in higher manufacturing costs. This can make mid-drive motor e-bikes less accessible for riders on a tight budget.
Lacks a Throttle:
Unlike some e-bikes with hub motors that may include a throttle mode, many mid-drive motor e-bikes operate solely on pedal-assist mode. This means that the motor provides assistance only when the rider is actively pedaling. While this is advantageous for a more natural and intuitive riding experience, it may be less appealing to riders who prefer the option of using a throttle to engage the motor without pedaling.
Which is best? A hub motor or Mid Motor?
The choice between a hub motor and a mid-drive motor for an electric bicycle depends on factors like riding preferences, terrain, and budget.
Hub Motor:
- Advantages: Simplicity, affordability, easy installation, regenerative braking.
- Considerations: Weight distribution, limited gear range, reduced torque.
Mid-Drive Motor:
- Advantages: Efficient power delivery, balanced weight distribution, better hill climbing, natural riding experience.
- Considerations: Higher cost, complex maintenance, lack of throttle.
Ultimately, the “best” motor type depends on your specific needs and priorities. If you prioritize affordability, simplicity, and ease of installation, a hub motor might be suitable. On the other hand, if you value efficiency, balanced weight distribution, and optimized performance for hilly terrain, a mid-drive motor could be the better choice.
Consider test riding different e-bikes with both types of motors to experience first-hand how they perform and determine which motor type aligns best with your riding preferences and requirements.
Source: https://www.magicyclebike.com/news/info/ebike-hub-motor-what-is-it-and-how-it-works
https://www.gazellebikes.com/en-us/blog/ebike-hub-vs-mid-drive